Common side effects(40% of patients or more)

|
- Short-term mouth sores that will need treatment with pain medications and sometimes narcotics
- Short-term or long-term dry mouth
- Neck skin changes
- Short-term or long-term change in taste
- Thickened mucus causing gagging
|
- Short-term post-surgical throat pain that will need treatment with pain medication including narcotics
- Short-term problems with swallowing
- Changes to appearance of neck (asymmetry)
- Ear numbness
|
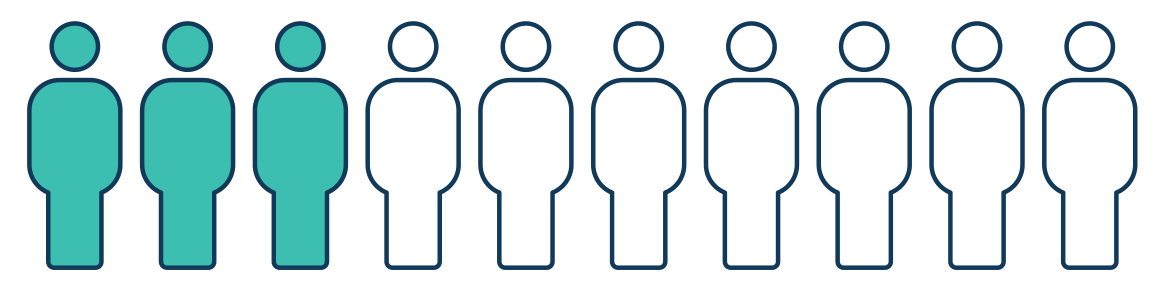
Somewhat common side effects(20 - 30% of patients)
|
- Swallowing issues that need a short-term feeding tube
- Dental cavities
- Thyroid issues that need medication
- Problems opening jaw widely
- A type of neck / face swelling called lymphedema
- Neck stiffness
- Short-term or long-term voice hoarseness
- Short-term or long-term hearing loss
|
- Short-term shoulder weakness or pain
- Short-term weakness of the lower lip
- Short-term neck stiffness
|
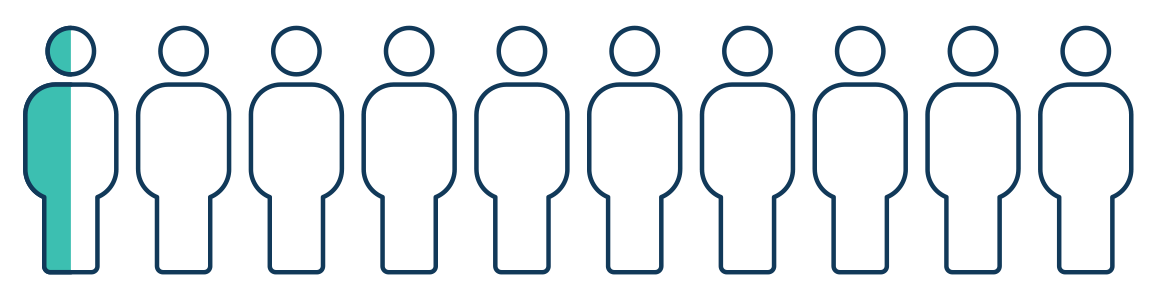
Less likely side effects(5% of patients)
|
- Long-term swallowing issues
- Jaw decay
- Long-term mouth sores
|
- Short-term spillover of swallowed food or drink into the back of the nose
- Permanent weakness of the lower lip
- Poor wound healing
- Infection
- Permanent shoulder weakness or pain
- Long-term swallowing issues
|
Very rare side effects(Less then 5% of patients)
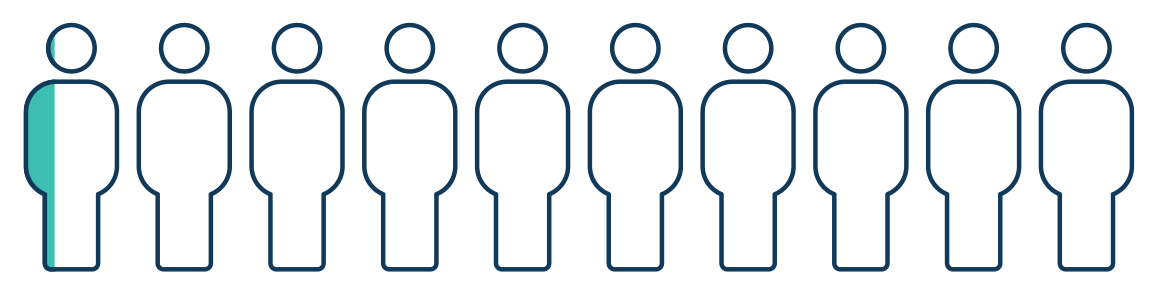
|
- Getting a second type of cancer
- Tongue weakness
- Shoulder weakness or other nerve damage
- Stroke
|
- Life-threatening bleeding
- Blood clots
- Side effects from anesthesia including death
- Permanent spillover of swallowed food or drink into the back of the nose
|